Space-Ray is a British company founded in 1949, specializing in low-consumption industrial heating systems using a gas radiant tube. In addition to providing energy savings of up to 70% over other forced air systems, Space-Ray radiant tube radiators are easily installable and require little maintenance.
Due to the internal combustion system, efficient Space-Ray radiant tube heating systems contribute to maintaining air quality, since they do not contaminate the environment with gases or harmful particles produced during the combustion of the gas.
Being a low-energy infrared heating system, Space-Ray radiant tubes generate a comfort similar to that produced by the sun’s rays.

What problem do gas radiant tubes solve?
They improve industrial productivity during the winter months
During the winter months, the entrance of cold air from outside causes the temperature of industrial buildings to fall, causing decreases in productivity, especially when it comes to precision work or when production processes require minimum work temperatures.
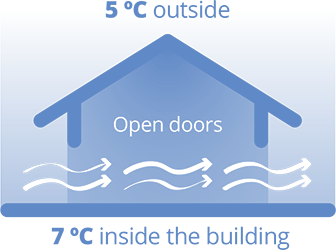
How does industrial heating by gas radiant tube work?
Through gas and infrared
The gas burner produces a flame that travels inside the tube, causing it to heat up at high temperatures. The aluminium diffuser projects the heat in the same way as the sun would. There is the possibility of sealed combustion. Without contaminating the environment with gases or harmful particles derived from the combustion of gas.
How do Space-Ray gas radiant tubes heat industrial buildings?
Sectorally and efficiently
We place the radiant tubes in work areas and distribute the heat only where it is necessary. Gas radiant tubes reduce heat loss in case of air flow since they are not designed to heat the environment, but the surface of a particular area.



What is the energy consumption of Space-Ray gas radiant tubes?
100% sustainable system
The gas radiant tubes project infrared rays directly on the surface of the areas that the customer wishes to heat. This means an energy saving of between 30% to 70% compared to forced air systems.
- This example has been calculated with 3 radiant tubes of 30 kW each. Each radiant tube consumes an average of 2.73 m3 of gas per hour, taking into account that the cost of the kW/h is € 0.05132 and that in an 8-hour working day the radiant tubes turn on an average of 5.8 hours.
What are the benefits of low-consumption industrial heating using Space-Ray radiant tubes?
![]()
Reduces CO2 emissions
Due to its lower energy consumption, efficient gas radiant tube heating can help reduce CO2 emissions.
![]()
Heating by zones
The low consumption heating by means of radiant tube heats zones individually thanks to its technology not requiring warming up all the environmental air to offer a sensation of comfort.
![]()
Low consumption heater
Gas radiant tube heating means energy savings of up to 60% compared to forced air heating systems.
![]()
Fast acting heating
Efficient heating systems using a gas radiant tube immediately heat up any environment since it is not necessary to heat the upper layers of air to feel an optimal comfort temperature.
![]()
Solar heat effect
Being an infrared heater, the Space-Ray gas radiant tube heater offers a feeling of comfort similar to the sun’s rays. Internal combustion eliminates the gases produced during combustion and offers maximum comfort.
![]()
100% directional heat
Efficient gas radiant heating systems can be installed both on ceilings and on walls and can be directed to generate heat wherever you want.
![]()
Efficient in the event of drafts
Because radiant tube heating does not base its action on heating the ambient air, but on directly heating the surface of the objects, it is an efficient system in environments where drafts are frequent.
![]()
Clean and healthy environment
The efficient heating of gas radiant tube keeps the environment clean and healthy thanks to its internal combustion chamber since it eliminates any residue from combustion directly to the outside.
For what type of industries are gas radiant tubes suitable?

- Industrial buildings and factories
- Automotive workshops
- Private homes
- Industrial laundries
- Cardboard packaging and printing industry
- Hotel and catering
- Poultry and pig farms
- Gyms and sports centres
- Shopping centres




